Home » Speciality » Heart Care
Best Heart Care
Hospital in India
offering comprehensive heart disease treatments.
Why choose Wockhardt Hospitals
for Heart Treatment?
Renowned Cardiologists
at Wockhardt Hospitals
- Mumbai Central
- Mira Road
- Nagpur
- Rajkot
What is Cardiology?
Cardiology is a superspecialty of internal medicine that deals with cardiac problems and abnormalities. It is the diagnosis and treatment of heart and cardiovascular problems. Congenital heart defects, heart failure, coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology are among the subclones of heart disease diagnosis and treatments covered in this field. Cardiology has several subspecialties, including nuclear cardiology, echocardiography, interventional cardiology and cardiac electrophysiology.
Cardiologists are doctors with a focus on treating heart problems and they are in charge of managing various cardiac conditions medically. The specialised doctors who carry out surgical heart disease treatments are called cardiac surgeons.
Signs and Symptoms
of Heart Disease
The term “heart disease” refers to a variety of heart-related conditions. Early signs of heart disease include:
- Chest pain.
- Fatigue.
- Shortness of breath.
- Palpitation
- Swelling in your legs.
- Dizziness, fainting unexpectedly or near-fainting repeatedly.
Depending on the type of heart condition you are dealing with, you may experience various heart disease symptoms.
Symptoms of abnormal heart rhythms
- Chest pain.
- Sweating.
- Pounding or racing heart
- Shortness of breath.
- Light headedness
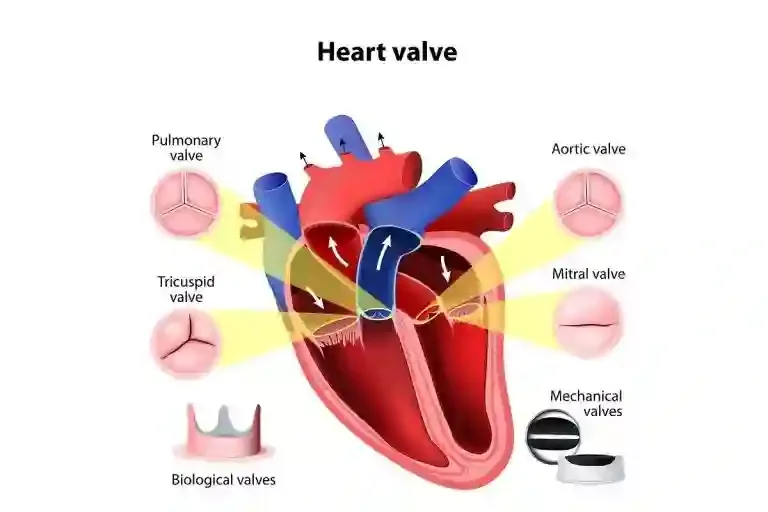
Symptoms of heart valve disease
- Chest pain.
- Dizziness.
- Tiredness.
- Shortness of breath.
Symptoms of heart pumping difficulties
- Swelling in your lower body.
- Shortness of breath.
- Difficulty sleeping.
- A sudden, unexpected loss of consciousness or dizziness.
Symptoms of blockages in your heart’s blood vessels
- Chest pain
- Neck pain/Jaw pain
- Exhaustion.
- Dizziness.
- Heartburn or indigestion.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Shortness of breath.
- Pain heaviness, or discomfort in your chest on exertion
Symptoms of congenital heart conditions
- Tiredness.
- Shortness of breath.
- Pale gray or blue skin or lips
- Inability to handle exercise.
Causes
of Heart Disease
Depending on its specific type, several factors might contribute to heart disease. Heart disease occurs in the following situations:
- Harm to the whole or a portion of the heart.
- A condition affecting the blood vessels that lead to or leave the heart.
- A difficulty with the heart's rhythm
- A lack of nutrients and oxygen reaching the heart.
Occasionally, a hereditary factor plays a role. Yet there are also some lifestyle choices and health issues that might raise the risk. A few of these include:

- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Overweight and obesity
- High stress and anxiety levels
- Consumption of alcohol or Smoking
- Dietary choices
- Age
- A family history of heart disease
- Sleep apnea
- Leaky heart valves
Common Medical Test to
Diagnose Heart Conditions
For heart disease diagnosis, a doctor will take a detailed medical history and conduct a physical examination, including listening for abnormal heart sounds, checking for chest congestion, and measuring blood pressure. Diagnostic heart disease tests are then performed to help identify the root causes of heart failure and guide heart disease treatment decisions.
- Blood Tests - It assists in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac diseases. It is possible to identify certain chemical indicators, such as the brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), which the heart secretes when it is overworked or wounded, troponin levels indicate myocardial infarction.
- Chest X-ray - An X-ray of the chest shows the heart and lungs. One can find, among other things, an enlarged heart or fluid in the lungs.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) - An electrocardiogram, commonly known as an EKG or an ECG, is a diagnostic instrument that captures the electrical activity of the heart and helps in the identification of irregular cardiac rhythms.
- Echocardiography - An essential diagnostic procedure called echocardiography uses sound waves to gauge the heart's capacity to pump blood and evaluate the condition of the organ's chambers and valves.
- Coronary Angiography - Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses a dye injection to detect heart artery narrowing, which may be causing heart failure. A ventriculogram, measuring the left ventricle's strength and assessing heart valve function, may also be performed during the exam.
- The nuclear heart scan (Radionuclide Imaging or Radionuclide Ventriculography) - The major blood arteries entering and leaving the heart are highlighted by the nuclear heart scan using radioactive tracers (such as technetium or thallium). It can be used to identify any heart muscle damage and to determine the presence of heart disease, valve issues, or heart failure.
- Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Cardiac Computed Tomography (CT) - New cardiac care imaging techniques such as MRI and CT allow for a more detailed examination of the heart and great vessels.
- Exercise tests or stress tests - The heart rate is measured while the patient walks on a treadmill or cycles on a stationary bike during these examinations. Exercise testing can assist in determining how the heart reacts to physical activity and whether experiencing exercise triggers heart disease symptoms.
How to Treat
Heart Disease?
It requires ongoing cardiology treatment. The heart’s ability to pump blood can be improved, as can the heart failure symptoms. Changes in lifestyle, medication, and occasionally surgery or devices that assist the heartbeat properly are all used as heart disease treatment options.
Medication
One or more medications used to treat heart failure may be included in prescription medication, such as:
- ARNI
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- Beta-blockers
- Digoxin (digitalis)
- SGLT 2 Inhibitors
- Statins
- Antiplatelet drugs
Surgery and medical devices
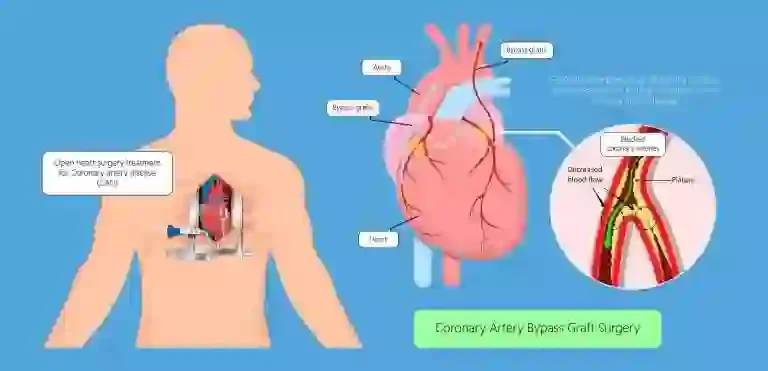
In order to address the underlying issue causing heart failure, surgery may be advised. A coronary artery block valve may need to be “fixed” by having it repaired or replaced.
- Angioplasty
- An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is a device that is placed beneath the skin and connected to the heart through thin cables. It keeps a watch on the heartbeat. If the heart begins to beat at a harmful rate, the ICD shocks it back into normal rhythm. In severe cardiac failure, a biventricular pacemaker is sometimes paired with an ICD.
- Cardiac resynchronization treatment (CRT), also known as biventricular pacing, transmits periodic electrical impulses to both bottom heart chambers (the left and right ventricles), coordinating their pumping and making it more efficient and coordinated.
- The damaged heart has to be replaced with a healthy donor heart in patients with severe heart failure who cannot be cured by surgery or medicine.
- Valve Replacement Surgery
- Surgery to correct congenital heart defects
- Pacemaker implantation
- Implantation of ventricular assist devices
- CABG
We Offer Quality Facilities
to Our Patients
- Ambulance Services
- Blood Storage Centres
- Cardiothoracic Intensive Care Unit
- Operation Suites
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Clinical Laboratory
Cardiology / Heart Care Blogs
FAQs on Heart Care
Q. How do I take care of the heart?
Keep the heart in a healthy condition by not smoking, consuming less alcohol, managing the stress: eating a balanced diet with reduced levels of saturated fats and cholesterol, and scheduling routine checkups. Make sure any chronic illness you have was taken care of and visit your doctor regularly to check your health condition.
Q. Can stress affect heart care?
Stress indeed can have considerable effects on the health of the heart. Chronic stress can lead to poor coping techniques such as binge eating, smoking or alcohol use, all of which raise the risk of heart disease. Similarly, stress hormones can also increase blood pressure and heart rate, which puts excessive strain on the cardiovascular system.
Q. How to prevent heart disease through certain lifestyle changes?
- Stop Smoking and Limit the intake of Alcohol
- Choose health diet
- Daily physical activity is advisable
- Be mindful of your weight
- Manage your diabetes
- Reduce stress
- Maintain your cholesterol level
- Get regular health checkups and heart disease test
Q. Is heart treatment possible without surgery?
Q. What is the cost of heart disease treatment in India?
In India, the average cost of medical procedures like CAGR or angioplasty used to treat cardiovascular problems ranges from Rs 3 lakhs to Rs 5 lakhs. Depending on how severe the condition is, the cost may increase significantly. We at Wockhardt Hospitals provide consultations that can be booked over our website or via a call to our hospitals. During this consultation, the doctor shall evaluate the need for the procedure and subsequently, one can discuss the cost and the procedure before scheduling one.
Q. I have other health conditions. How do I manage them together?
Q. What are the risk factors of heart disease?
- High cholesterol.
- High blood pressure.
- Inactive lifestyle.
- Use of Tobacco products
- Type 2 diabetes.
- Heart disease in your family.
- Having excess weight or obesity.
- Substance use disorder.
- Unhealthy Diet
Q. How can I make my heart strong?
By addressing risk factors and altering one’s lifestyle, heart disease can mostly be avoided. One can maintain a strong heart by incorporating the following suggestions into their daily life:
- Consume a balanced, well-rounded diet.
- Avoid prolonged sitting.
- Keep your weight in check.
- Quit smoking and stay away from secondhand smoke.
- Ensure proper rest at night.
- Identify your stressors and take steps to manage them.
Q. What is the success rate of heart treatment in India?
Q. What are some heart-healthy foods?
The following foods are among the most beneficial for maintaining a strong and healthy heart:
- Olive oil
- Walnuts
- Almonds
- Sweet Potatoes
- Oranges
- Low-fat Yogurt
- Dark leafy greens such as Spinach