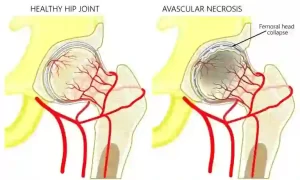
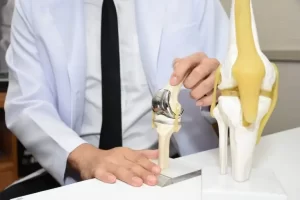
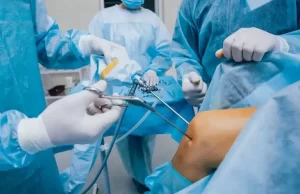
Avascular necrosis (AVN) of the femoral head, commonly known as osteonecrosis, is a condition that affects the hip joint, primarily impacting the blood supply to the bone. Left untreated, it can lead to pain, disability, and even the need for orthopedic treatment. As an orthopedic surgeon at Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai Central, I believe in empowering patients with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their health. In this article, we will explore the stages of AVN and discuss the importance of seeking timely treatment. Additionally, we will shed light on the Direct Anterior Approach to hip replacement, a cutting-edge surgical alternative that offers early functional recovery for individuals dealing with this condition. What is Avascular Necrosis? The death of bone tissue as a result of inadequate blood flow is known as avascular necrosis. It is also referred to as ‘osteonecrosis’, and it can produce small fractures in the bone, eventually causing it to break down. The interruption or lack of blood supply causes bone tissue to break down, often resulting in pain, restricted movement, and, in severe cases, collapse of the affected bone. Commonly affecting the hip, knee, shoulder, and other joints, it can be triggered by injury, excessive alcohol consumption, steroid use, or underlying medical conditions. Anybody can get impacted. However, individuals between the ages of 30 and 50 are more likely to suffer from this condition. Early detection through imaging tests and timely intervention, such as medication, physical therapy, or surgery, is crucial to manage symptoms and prevent further damage. Symptoms of Avascular Necrosis Femoral Head Depending on the stage and the damaged bone, AVN symptoms might vary. Some individuals with avascular necrosis have no symptoms at all in the initial phases. As the condition worsens, the affected joints might hurt only when you put weight on them. After a while, the pain could even be too much to handle when you’re resting. Typical indications consist of: Causes of Avascular Necrosis Femoral Head Avascular necrosis is brought on by diseases or bone fractures that obstruct blood supply to bone tissue. Avascular necrosis can result from a number of disorders or treatments, including: Nontraumatic AVN is also linked to the following conditions: Treatment of Avascular Necrosis Femoral Head The extent of damage in the bones will determine the course of treatment. Enhancing function and preventing more bone or joint deterioration are the two main objectives of therapy. If the extent of your bone deterioration is restricted to smaller, non-weight-bearing bones, your doctor may consider the following treatments: Patients with more severe cases of avascular necrosis may require surgery to treat their conditions. Among the surgical possibilities are: How is Avascular Necrosis Diagnosed? Diagnosing avascular necrosis (AVN) involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests to assess the affected joint and confirm the presence of bone tissue damage. The diagnostic process typically includes: Medical History and Physical Examination: The doctor will inquire about symptoms, medical history, medications, and any past injuries or treatments. A doctor or nurse will examine your joints during a physical examination to check for any soreness. In order to determine if the range of motion is reduced, they may also rotate the joints through various positions. Imaging Tests: Various imaging techniques are employed to examine the affected bone and assess its condition: Biopsy: In rare cases, a sample of bone tissue may be extracted and examined under a microscope to confirm AVN diagnosis, although this is less commonly performed due to the accuracy of imaging tests. What are the Risk Factors for Osteonecrosis? Several factors increase the risk of developing osteonecrosis. Understanding these risk factors is crucial in identifying individuals who might be more susceptible: How to Prevent Avascular Necrosis? Preventing avascular necrosis (AVN) involves addressing underlying risk factors and adopting proactive measures to safeguard bone health and circulation. Consider these strategies to help reduce the risk: Understanding AVN Stages AVN progresses through stages that indicate the severity of the condition. Early detection and intervention are crucial for successful treatment. Here are the stages of AVN: 1. Initial Stage: In this stage, the blood supply to the femoral head is compromised, leading to cellular damage. At this point, the bone structure remains intact, and symptoms might not be noticeable. However, early diagnosis through imaging (X-rays, MRI) can identify subtle changes, enabling timely intervention. 2. Necrosis Stage: Blood flow continues to be restricted, causing the bone tissue to die (necrosis). Patients may start experiencing pain and discomfort during this stage, particularly with weight-bearing activities. Conservative treatments, such as medication, rest, and limited weight-bearing, might be recommended. 3. Crescent Stage: The dead bone weakens and might collapse, leading to a crescent-shaped fracture. Pain and limited range of motion become more pronounced. Surgical interventions, such as core decompression, may be considered at this point to alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage. 4. Flattening Stage: The femoral head loses its shape and flattens due to the ongoing collapse. Joint function significantly deteriorates, leading to more intense pain and reduced mobility. Joint-replacement surgery may be advised to restore function and relieve pain. 5. Advanced Stage: The final stage involves extensive damage to the femoral head, causing severe pain, disability, and joint dysfunction. Total hip replacement surgery becomes a more likely option to restore mobility and quality of life. Seeking Timely Treatment in India In India, timely treatment of AVN is of paramount importance, considering the prevalence of conditions that may contribute to AVN, such as trauma, corticosteroid use, alcoholism, and certain medical conditions. If you experience persistent hip pain, limited range of motion, or discomfort during movement, it’s crucial to consult a qualified orthopedic specialist. Prompt diagnosis through medical imaging and comprehensive evaluation can determine the stage of AVN and guide appropriate treatment. Depending on the stage, treatment options may include medication, lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, core decompression, joint-preserving surgeries, or hip replacement. Direct Anterior Approach: Revolutionizing Total Hip Replacement When AVN progresses to the point where joint-preserving treatments are no longer effective, hip replacement surgery