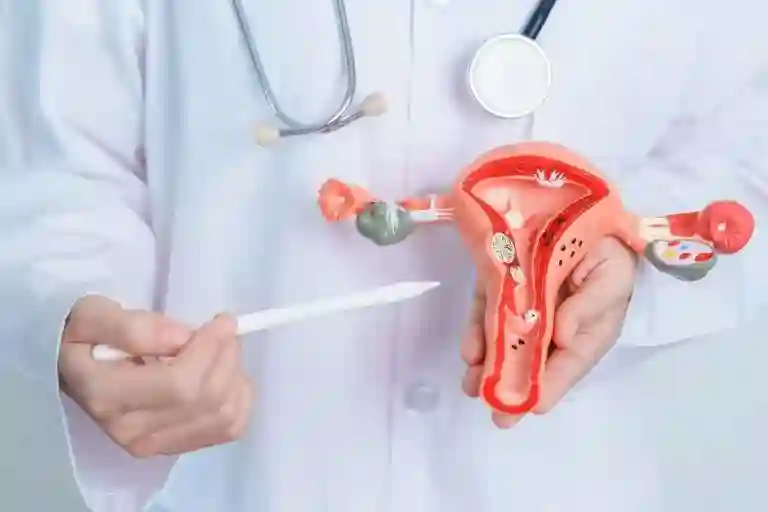
Endometrial cancer, commonly referred to as uterine cancer, is a specific type of cancer that originates within the uterus. The uterus is a crucial female reproductive organ, characterised by its hollow, pear-shaped structure located in the pelvic region. It serves as the nurturing environment for foetal development during pregnancy.
Endometrial cancer initiates in a specific layer of cells that form the lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium. One distinguishing feature of endometrial cancer is that it is often detected at an early stage due to a noticeable symptom: abnormal vaginal bleeding. This irregular bleeding is a red flag and one of the main uterine cancer signs that prompts many individuals to seek medical attention, leading to the diagnosis of endometrial cancer.
In cases where endometrial cancer is identified in its early stages, the doctors employ a surgical technique called hysterectomy i.e., the removal of the uterus, for its treatment. With this, the doctors aim to remove the cancer’s source and prevent metastasis.
Types of Uterine Cancer
Cancer in the female reproductive system may appear at any of the parts, based on which there can be different types of uterine cancer.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer develops in the endometrium and is the most common gynaecological cancer affecting the female reproductive system.
Uterine Sarcoma
Tumours developing in the myometrium, which is the muscle wall of the uterus, are known as uterine sarcomas. These are rare gynaecological cancers.
Cervical Cancer
Cancer develops in the cervical part of the uterus, which is located at the end of the uterus. This is called cervical cancer, as it affects the cervix of the uterus.
What Causes Uterine Cancer?
While the exact uterine cancer causes are still not known, certain factors can increase a woman’s risk of developing this condition. Getting a comprehensive understanding of potential uterine cancer causes can be beneficial in preventing the disease in the first place. It can also help in early detection and prompt treatment. Some uterine cancer causes and risk factors are as follows:
- Age: Endometrial cancer cases are high in women who have gone through menopause and typically in their mid-60s or older. This is due to the hormonal changes accompanied by a menopause.
- Hormone Levels: The risk of endometrial cancer is influenced by hormone levels in the body. The risk chiefly increases due to an imbalance in the hormones progesterone and oestrogen. The presence of excess oestrogen in the body without a proper counterbalance of progesterone results in the thickening of the endometrial lining within the uterus.
- Genetics: Genetic factors that are inherited can also contribute to the risk of endometrial cancer. Lynch syndrome, for example, is a hereditary condition caused by a mutation in a specific gene that tends to run in families. This genetic mutation puts a woman at increased risk of endometrial cancer, in addition to other types of cancer.
- Being Overweight: An unhealthy body weight can contribute to the development of uterine cancer. A BMI of 25.0 and above is linked with higher chances of uterine cancer. To reduce the risk of endometrial cancer, maintaining a healthy body weight is crucial.
Uterine Cancer Signs and Symptoms
Uterine cancer or endometrial cancer may exhibit certain symptoms of uterine cancer, but the type of uterine cancer symptoms one may experience and their intensity may vary based on the stage of the cancer, among other factors. In addition, the signs can sometimes be hard to recognise as they are very similar to those of certain other reproductive conditions. However, it is essential for women to be aware of symptoms of uterine cancer to recognise the condition in time and prevent potential complications that may arise. On that note, listed below are the endometrial cancer symptoms experienced by women at different stages of the condition:
Stage I (Confined to the Uterus):
- In the initial stage, most women experience no symptoms of uterine cancer as such. At Stage 1, when the cancer is limited to the uterus, cancer is typically asymptomatic.
- Some women may experience profuse or abnormal bleeding. Abnormal bleeding may occur during the menstrual cycle, during sex, or after menopause.
- In very rare circumstances, pelvic pain or lower abdominal pain may occur.
Stage II (Spread to the Cervix):
- In the second stage, when the cancer spreads to the cervix, women may notice more symptoms of uterine cancer.
- Abnormal and profuse bleeding may intensify at this stage, and may occur at the aforementioned instances.
- Women may experience intensified abdominal pain while performing normal activities or while having sex.
- Vaginal discharge may also occur, and the consistency may vary from the normal consistency.
Stage III (Spread to the Vagina, Ovaries, and/or Lymph Nodes):
- At stage 3, cervical or endometrial cancer progresses to nearby structures, such as the vagina, ovaries, or lymph nodes. This may cause the symptoms of uterine cancer to become more severe.
- Abnormal bleeding may continue, and become more profuse.
- Women may experience more severe vaginal discomfort, which may be consistent or happen in intervals.
- A condition called lymphedema i.e., a swelling or enlargement of the legs, may also occur. This happens as a result of the involvement of lymph nodes.
Stage IV (Spread to Distant Organs):
- A stage IV endometrial cancer is recognised by the advancement of the cancer to distant organs such as the rectum and bladder. The symptoms of uterine cancer at this stage can be very severe and medical intervention is absolutely necessary.
- Women generally report issues such as frequent and painful urination and blood in the urine. Pelvic pain is also common.
- Rectal bleeding, painful bowel movements, and severe constipation may also result due to the metastasis of cancer to the rectum.
Note: While the signs and symptoms discussed can mimic those of other conditions, it is essential for anyone experiencing them to seek prompt medical intervention. When diagnosed in time, endometrial cancer can be reversed.
Conclusion
Being diagnosed with uterine cancer can be frightening. But, it should be noted that it can be treated if prompt medical intervention is sought. Wockhardt Hospitals welcomes individuals who may suspect uterine cancer by recognising its symptoms in time. Our healthcare facility boasts a world-class team of highly reputable oncologists and gynaecologists, who provide personalised and all-round care for patients with uterine cancer. With the active participation of healthcare professionals from various departments, we adopt a holistic approach to the management of uterine cancer. Your health is our utmost priority, and we are here to provide exceptional care at every step of your treatment journey.
FAQs on Uterine Cancer
Q. What are the stages of uterine cancer?
Uterine cancer has four stages:
- In stage 1, the cancer is confined to the uterus.
- In stage 2, the cancer spreads to the cervix.
- Stage 3 involves the spread of the cancer to the vagina and ovaries, and
- Stage 4 is when the cancer spreads to the urinary bladder, rectum, or other organs.