Home » Medical Procedure » Coronary Angiography
Coronary Angiography Procedure
at Wockhardt Hospitals
What is
Coronary Angiography?
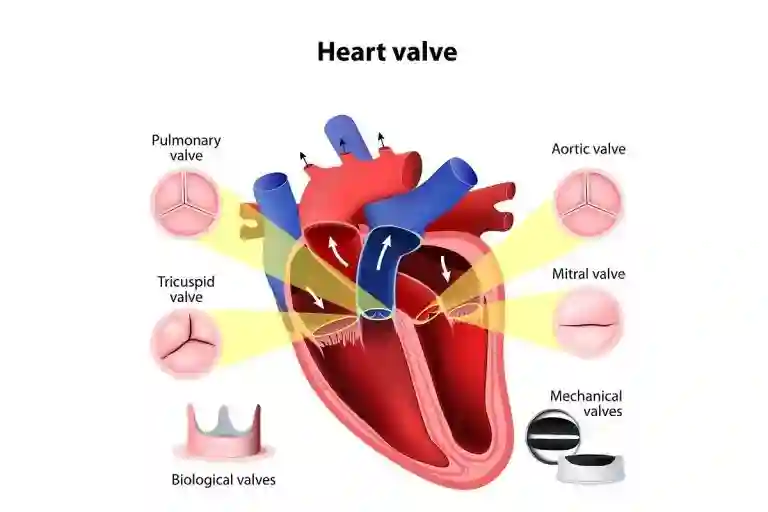
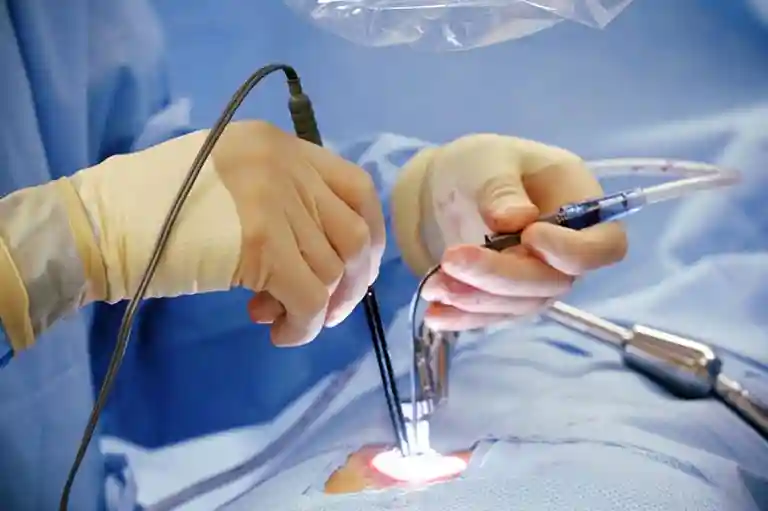
Coronary Angiography is a medical procedure used to diagnose and evaluate the severity of coronary artery disease. This diagnostic procedure involves inserting a catheter into an artery in the arm or groin and threading it up to the heart. A contrast agent is then injected through the catheter, and X-ray images are taken to visualize the coronary arteries.
Coronary Angiography is usually recommended for individuals who have symptoms of coronary artery disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or heart palpitations. It is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of other heart treatments, such as bypass surgery or stent placement, and to assess the current situation of heart disease. While the procedure carries some risks, the benefits of accurately diagnosing and treating coronary artery disease typically outweigh these risks. Moreover, the highly experienced and board-certified medical professionals at Wockhardt Hospitals use the most advanced tools & equipment to perform Coronary Angiography in India. They are backed by cutting-edge infrastructure to reduce the risks and get precise results.
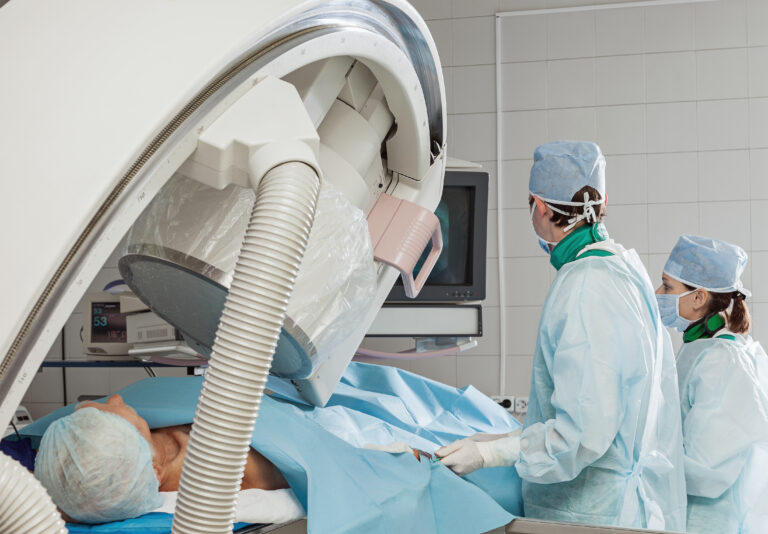
Renowned Coronary Angiography Surgeons
at Wockhardt Hospitals
- Mumbai Central
- Mira Road
- Nagpur
- Rajkot
Why is the Coronary Angiogram done?
A Coronary Angiography procedure is typically done to evaluate the extent of coronary artery disease (CAD), which is a condition where arteries that supply blood to the heart become blocked/narrowed. The procedure helps identify any blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries that can restrict blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and even a heart attack.
The procedure can also be done to assess the effectiveness of previous treatments, such as stent placement or bypass surgery, and to evaluate the severity of heart valve disease. Additionally, it may be done for individuals who have abnormal results on noninvasive cardiac tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or stress test.
Overall, Coronary Angiography is a valuable tool for diagnosing and treating heart disease, and it can help physicians create the best course of treatment for their patients, including medications, lifestyle changes, or further procedures.
What are the
advantages of Angiography?
There are various benefits that Coronary Angiography can offer.
- Helps to diagnose and evaluate the extent and severity of coronary artery disease (CAD).
- Identifies any blockages/narrowing in the coronary arteries that can restrict blood flow to the heart.
- Can potentially prevent a heart attack or other serious complications by identifying and treating CAD.
- Assesses the effectiveness of treatments, such as stent placement or bypass surgery.
- Evaluates the severity of heart valve disease.
- Helps physicians determine the best course of treatment for their heart patients.
What are the
Different Types of Angiograms
There are several types of angiograms, including:
- Coronary Angiogram: It is used to visualize the coronary arteries in the heart.
- Cerebral Angiogram: It is to assess the blood vessels in the brain.
- Pulmonary Angiogram: It is performed to visualize the blood vessels in the lungs.
- Renal Angiogram: It is to visualize the blood vessels in the kidneys.
- Peripheral Angiogram: It assesses the blood vessels in the arms, legs, or other body parts.
How is a Coronary
Angiogram performed?
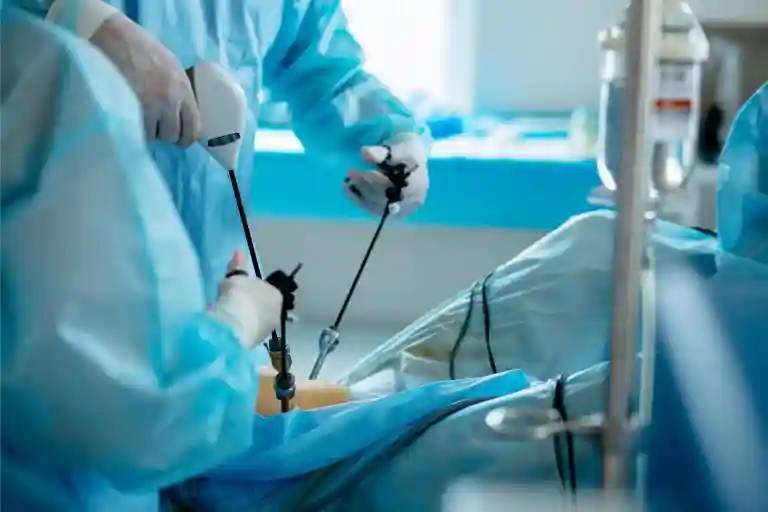
Coronary Angiography process is usually performed in a safe and fully equipped room at Wockhardt Hospitals by an experienced cardiologist or radiologist. The procedure typically takes about 30-60 minutes to complete the Coronary Angiography test and involves the following steps:
- The concerned patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the operative area where the catheter will be inserted (usually in the arm or groin).
- A sheath is inserted into the artery, and a catheter is threaded through the sheath and up to the heart.
- A contrast agent is then injected through the catheter, and X-ray images are taken to visualize the coronary arteries & identify any blockages or narrowing.
- The catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the insertion site to prevent bleeding.
- The patient is monitored for several hours after the procedure to check for any complications.
The patient may feel some pressure or discomfort as the catheter is inserted but should not experience any significant pain. After the Coronary Angiography procedure, the patient may experience some soreness or bruising at the insertion site, but these symptoms usually resolve within a few days. The angiogram results are usually available within a few hours and will be discussed with the patient by their healthcare provider.
Before Coronary Angiography
Before an Angiography procedure, the patient will typically have an appointment with their cardiologist to discuss the procedure and review their medical history. The patient may also need to fast for several hours before the procedure, as instructed by their healthcare provider.
In addition, the patient may undergo some preparatory tests, such as blood tests or an electrocardiogram (ECG), to assess their overall health and ensure they are a good candidate for the procedure. The healthcare provider may also review the patient’s medical records to check for any underlying health conditions or allergies that could affect the procedure.
On the procedure day, the patient should wear comfortable, loose clothing and avoid wearing any jewellery or other accessories that may interfere with the procedure. The patient may be given a mild sedative to help them relax during the procedure and must arrange for someone to drive them home afterward.
It is important for the patient to inform their healthcare provider of any medical conditions or allergies they have, as well as any medications they are taking, including over-the-counter medications, vitamins, or supplements. The patient should also inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or breastfeeding.
During Coronary Angiography
The patient is awake during the procedure but given a mild sedative to help them relax. The procedure involves the insertion of a catheter through a sheath in the arm or groin and up to the heart. Contrast dye is injected through the catheter, and X-ray images are taken to visualize the coronary arteries. The patient may feel some pressure or discomfort during the procedure but should not experience significant pain.
After Coronary Angiography
After a Coronary Angiography procedure, the patient will typically remain in the hospital for a few hours for observation. Our healthcare providers will monitor the insertion site for any bleeding or other complications and may recommend that the patient lie flat for a certain period of time to minimize the risk of bleeding. The patient may also be given pain medication or a cold compress to reduce discomfort or swell at the insertion site.
The patient should avoid strenuous activity or heavy lifting for at least 24-48 hours after the procedure and may need to avoid driving for a short period. The patient should follow sanitary habits and keep the operational site dry and clean. Our doctors at Wockhardt Hospitals provide post-operative recovery instructions and other necessary follow-up care through follow-up appointments or adjusting medications.
How to Prepare Yourself for Fast
Recovery after Coronary Angiogram?
To prepare for a fast recovery after a coronary angiogram, it is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for rest and activity and to avoid strenuous exercises for at least 24-48 hours after the procedure. Eating a healthy diet and staying hydrated can also help promote healing and reduce the risk of complications. If the patient experiences any symptoms, such as fever, swelling, or redness at the insertion site, chest pain, or shortness of breath, they should contact their healthcare provider right away.
What are the
Risks Of a Coronary Angiogram?
While Coronary Angiography is generally a safe and well-preferred procedure, there are some risks and potential complications associated with it. These may include bleeding or bruising at the insertion site, allergic reactions to the contrast dye, kidney damage from the dye, heart rhythm disturbances, infection, stroke, or heart attack. The chances of complications are generally low, and most people recover quickly and without any significant problems. However, it is important for patients to be aware of the potential risks and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider before the procedure.
Talk with our expert
Life Wins Stories
The vision and leadership of Wockhardt’s Founders have been instrumental in shaping the organisation’s ethos of providing high-quality and affordable healthcare services to patients worldwide. Read and listen to the heartfelt experiences of our patients as they share their stories about the exceptional care they received at Wockhardt Hospitals.


Paresh Vyas
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.

Meena Kothari
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.
Life Wins Stories

Paresh Vyas
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.

Meena Kothari
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.