Potassium is an important electrolyte in the body and is responsible for the function of muscles, nerves, and the heart. Very low levels of potassium are called hypokalaemia and can lead to dangerous consequences as a person may even feel too weak to move their body, experience paralysis, faint, or experience irregular heart rhythms. Vomiting, diarrhea, or use of laxatives can lead to low potassium levels while certain medications like diuretics that are commonly used to treat high blood pressure can also eliminate potassium along with excess sodium and water from the urine.
In hypokalemia, the amount of potassium in the blood is too low. The normal levels of potassium range from 3.5 to 5.2 mEq/L (3.5 to 5.2 mmol/L). Anything lower than 3 mEq/L (3 mmol/L) can be considered severe hypokalaemia. While mild cases of hypokalaemia are asymptomatic, in case of dangerously low levels of potassium, one must get medical attention.
Low Potassium Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of low potassium depend on the severity of hypokalaemia. Mild cases are usually asymptomatic i.e., when potassium is 3-3.5 meq/l or unless the patient is either elderly or has other major medical problems like chronic kidney disease or heart failure. Symptoms usually appear once Serum K levels go below 3.0 meq/l.
Dr. Bhuwania explains in detail the symptoms of hypokalaemia:
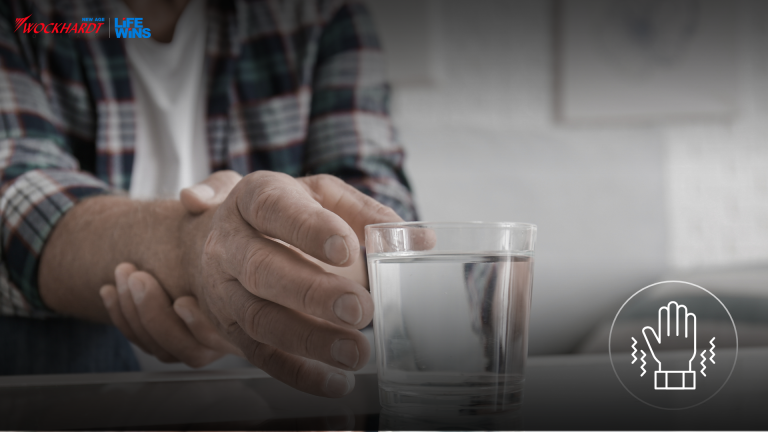
- Neurological: Muscle cramps and limb weakness particularly in lower limbs; may cause a paralysis-like state.
- Gastrointestinal: Constipation and abdominal distension, nausea, and vomiting.
- Generalized fatigability and myalgia
- Cardiac: Low blood pressure, palpitations due to irregular heart rates related to atrial and ventricular arrhythmias
- Respiratory muscle weakness and in severe cases respiratory failure.
Low Potassium Causes
“Low potassium levels, also known as Hypokalaemia, occur when the level of potassium in the serum falls below the normal range of 3.5-5 meq/l. Potassium is one of the major electrolytes in the body, which has a direct role in the proper functioning of the heart muscle, skeletal muscles, and intestinal activity. Low potassium levels can lead to disturbances in these functions due to its role in normal cell functioning,” said Dr Kamal Verma, Senior Consultant, Department of Internal Medicine, Amrita Hospital, Faridabad.
“A significant decrease in potassium levels, particularly in persons with heart disease, may result in irregular cardiac rhythms. This might cause you to feel dizzy or faint. A low potassium level might even cause your heart to stop beating. Potassium is required to maintain your muscles, neurons, and heart functioning properly. Potassium is also required for a healthy digestive system and bone health. Potassium deficiency can impair these vital bodily activities. Low potassium levels in the body can induce irregular heart rhythms, muscular weakness, and even paralysis over time,” Dr. Puneet Bhuwania, Consultant Nephrologist & Transplant Physician at Wockhardt Hospitals, Mira Road.
Low Potassium Treatment
- Potassium-rich diet: Fruits like bananas and oranges, green leafy vegetables, potatoes, and kiwi.
- Oral potassium supplements as per doctor’s advice.
- Patients may need hospitalization in case of severe hypokalaemia as per the treating physician’s decision.
Dr. Puneet Bhuwania
Consultant Nephrologist & Transplant Physician
Wockhardt Hospitals, Mira Road
To book an appointment call: +918108101104
FAQs on Low Potassium
Q. What happens if your potassium is low?
Many health problems, including weariness, constipation, tingling feelings, irregular heart rhythms, muscular cramps, and muscle weakness, can be brought on by low potassium levels. Paralysis or respiratory failure are possible outcomes in severe instances.
Q. How can I raise my potassium quickly?
Q. What organ is affected by low potassium?
Q. What are the symptoms of low potassium in females?
Q. What are the 10 signs of low potassium?
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle Cramps
- Fatigue and nausea
- Abnormal heartbeats
- Constipation
- Tingling or numbness
- Low blood pressure
- Excessive urination (polyuria)
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Paralysis in severe cases