Insulin Resistance: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
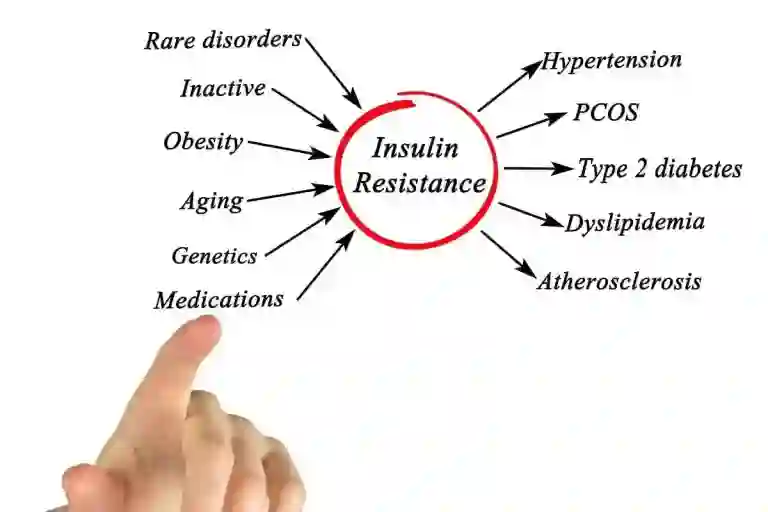
Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its association with various health problems, including obesity, Type-2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. It revolves around the hormone insulin, which is essential in controlling blood sugar levels. It is a complicated yet critical part of human physiology. Insulin resistance is a condition in which the fat, muscles & liver cells do not respond to insulin as expected and are, therefore, unable to use blood glucose for energy. The pancreas produces an extra amount of insulin to make up for the loss, and the levels of blood sugar rise over time. Below are the various factors to consider. Insulin Resistance Symptoms Insulin resistance is often referred to as a “silent” condition because it can develop slowly and progress without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition worsens, variousinsulin resistance symptoms may become evident. It is important to be aware of these symptoms as early detection and intervention can help prevent the development of more severe health problems. Some common symptoms of insulin resistance include: Insulin Resistance Causes Insulin resistance is a multifaceted condition with various contributing factors. While genetics can be a possible cause, lifestyle choices are often the primary drivers of insulin resistance. Some common insulin resistance causes include: Insulin Resistance Brought on by Hormonal Issues Our body’s ability to utilize insulin can be impacted by problems with certain hormones. Among the hormonal conditions that might result in insulin resistance are: Insulin Resistance Treatment The goal of insulin resistance treatment is to increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, control blood sugar levels, and lessen the hazards to one’s health. Adopting a thorough strategy that incorporates dietary adjustments and, in certain situations, medicinal treatments is essential. The insulin resistance treatment that are mainly used are listed below: Why is Wockhardt Hospital considered the Best for the Treatment of Insulin Resistance? Wockhardt Hospitals has a great reputation in India as a prominent healthcare center, providing comprehensive and innovative care for those suffering from insulin resistance and associated disorders. The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic facilities, enabling accurate and timely diagnosis for insulin resistance treatment. The hospital offers a comprehensive range of services, from dietary counseling and exercise therapy to medication management and surgical interventions when necessary. This multifaceted approach ensures that patients receive well-rounded care.
Brittle Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Brittle diabetes is a rare and severe form of diabetes that poses unique challenges for both patients and healthcare professionals. It is a particularly challenging and less well-known subtype of Diabetes, which itself is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is sometimes referred to as labile or unstable diabetes because of the possibility of significant and frequent blood sugar changes. Brittle diabetes patients experience significant swings in their blood glucose levels. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) episodes may occur often as a result of the fluctuations. These unpredictable changes can lead to a variety of complications and make daily life exceedingly challenging for those affected with brittle diabetes, also known as labile or unstable diabetes. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes are most likely to develop brittle diabetes (with Type 1, the body does not manufacture insulin). It most commonly affects women in their 20s and 30s for unexplained causes. Causes of Brittle Diabetes Understanding the brittle diabetes causes is essential for effectively managing and treating this complex condition. The brittle diabetes causes are multifactorial and can vary from person to person: Brittle Diabetes Symptoms Recognizing the brittle diabetes symptoms is crucial in seeking early diagnosis and effective brittle diabetes treatment. Some people are unable to detect hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia when it occurs in their bodies. Signs of Hypoglycemia Individuals with brittle diabetes often experience episodes of low blood sugar, which can lead to brittle diabetes symptoms like shakiness, sweating, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Hypoglycemia affects people differently. The following are typical warning symptoms of excessively low blood sugar: The symptoms of hypoglycemia that worsen with time include: Signs of Hyperglycemia Compared to hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia’s symptoms might be less severe. Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), a potentially fatal condition that can develop from untreated high blood sugar, is one such possibility. When someone has DKA, their liver creates acids known as ketones. In the body, these acids can accumulate to dangerous levels. Signs of DKA Treatment of Brittle Diabetes Managing brittle diabetes is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. The primary goals of brittle diabetes treatment are to stabilize blood sugar levels, prevent severe fluctuations, and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some key components of brittle diabetes management at Wockhardt Hospitals: Why choose Wockhardt Hospitals for the management of Brittle Diabetes? The complicated and difficult disease of brittle diabetes calls for specialized treatment and a holistic approach to management. For people looking for the best care for this rare but difficult disease, Wockhardt Hospitals are a great option since they offer a thorough and patient-centered approach to treating brittle diabetes and diabetes surgery. They strive to continue to lead medical innovations. The hospital participates in clinical research and keeps up with the most modern advances in the management of diabetes in order to offer the best care possible.
Diabetic Coma: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment

Diabetes is a common health condition in patients in which the blood glucose level rises. Diabetes-related coma or diabetic coma is a life-threatening condition that leads to unconsciousness or unresponsiveness as a result of a very high blood glucose level (hyperglycemia) or very low blood glucose level (hypoglycemia) in a diabetic person. Diabetic coma requires immediate medical attention to be treated with success. However, it is best to prevent it by managing diabetes well. What is a Diabetic Coma? A diabetic coma is a diabetes-related complication that occurs as a result of unregulated blood glucose. It can occur due to very high, unregulated blood sugar levels, also known as hyperglycemia, or may also be caused by very low blood glucose levels, also known as hypoglycemia. Diabetic coma leads to a prolonged state of deep unconsciousness. Diabetic Coma Causes Generally, three types of diabetes-related complications may lead to diabetic coma, which may include: Diabetic Coma Symptoms The symptoms of high or low blood sugar in a person are usually present before the condition worsens and leads to a diabetes-induced coma. Symptoms of high blood glucose levels may include: Symptoms of low blood glucose level may include: These symptoms may worsen over time and lead to diabetic coma if diabetes of any kind is not managed and controlled properly. Diabetic coma symptoms mainly include three indications mentioned below. While the person is entirely unresponsive, there may still be some form of reflex response without storing any active memory of it. Since DKA (or Diabetic Ketoacidosis) may also lead to diabetic coma, it may exhibit some severe symptoms before it leads to a coma. HHS (or Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State) is another condition that may lead to diabetic coma symptoms, such as Risk Factors of Diabetic Coma Undiagnosed or unregulated diabetes leading to severely low or high blood glucose levels may lead to diabetic coma. The risk of diabetic coma depends on the type of diabetes: There are many other factors that may increase the risk of diabetic coma, which may include the following. Diabetic Coma Diagnosis A diabetic coma or diabetes-related coma is a medical emergency that requires medical intervention in the hospital. Healthcare providers or doctors may be able to diagnose diabetic coma by knowing the patient’s medical history and performing a blood glucose test that confirms the glucose level in the blood. They may also perform other tests to look for the level of ketones in the blood and the patient’s overall health condition. Diabetic Coma Treatment Diabetic coma treatment depends on the condition that has caused it. However, almost all cases of diabetic coma require medical treatment in the hospital. Diabetic coma caused by DKA or HHS may be treated by: Diabetic coma caused by high blood sugar may be treated by: Diabetic coma treatment of diabetic coma caused by low blood sugar may include giving a boost of glucagon, which can help the blood sugar level rise quickly. Preventing Diabetic Coma Managing diabetes is extremely crucial to prevent diabetic coma or any other complication of diabetes, for that matter. At Wockhardt Hospitals, medical emergencies and routine procedures are promptly attended to by a well-experienced team of primary care and emergency care doctors and specialists 24×7 to tend to all kinds of medical emergencies. Our specially dedicated ward of ICU and emergencies caters to every need of our patients, who are well taken care of by capable nurses and other supporting healthcare professionals for optimal recovery and management of the health problem.
Diabetes Hypoglycemia Diagnosis, Treatment & Surgery

Hypoglycemia, usually referred to as low blood sugar or low blood glucose, occurs when the concentration of glucose (sugar) in an individual’s bloodstream falls below the standard range. It is a common occurrence in individuals with diabetes, particularly Type 1 diabetes. This condition makes immediate hypoglycemia symptoms treatment requisite. The patients must consume sugar or carbohydrates if they have an episode of low blood sugar. What is Diabetes Hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia frequently occurs among individuals with diabetes, particularly those who use insulin as part of their diabetes treatment. Severe hypoglycemia can be life-threatening and demands intervention through the administration of emergency glucagon or medical care. For most individuals with diabetes, hypoglycemia is identified and diagnosed as having a blood sugar level below 70 mg per deciliter (mg/dL) or 3.9 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). For most individuals without diabetes, hypoglycemia is recognized as having a blood sugar level below 55 mg/dL or 3.1 mmol/L. What are the Causes of Diabetes Hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia can be caused by several factors. These factors might differ from patient to patient and include both medical reasons and lifestyle habits. Some causes of hypoglycemia are listed below: What are the Signs & Symptoms of Diabetes Hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia symptoms can manifest rapidly and differ among different individuals. Additionally, a person may experience distinct symptoms during each episode of low blood sugar. The low blood sugar symptoms serve as essential warnings, prompting one to seek hypoglycemia treatment before the blood sugar levels further decline. Some diabetes hypoglycemia symptoms include: How is Diabetes Hypoglycemia Diagnosed? When individuals exhibit symptoms of hypoglycemia, doctors can often diagnose the condition through low blood glucose measurements during symptomatic episodes. Blood tests are done to gauge glucose levels in individuals with diabetes. In the case of healthy individuals without diabetes, doctors can typically diagnose hypoglycemia based on symptoms, medical history, a physical examination, and basic glucose level measurements. Confirmation of hypoglycemia in non-diabetic individuals involves detecting low blood glucose levels along with typical symptoms, particularly if this correlation is observed on multiple occasions. In some other cases, when the results are unclear with the aforementioned assessments, additional diagnostic tests, such as fasting for blood glucose measurements in a closely supervised environment, may be necessary. Diabetes Hypoglycemia Treatment Diabetes treatment involves a multifaceted approach. When the symptoms appear, immediate medical intervention is required to raise the sugar levels. In severe cases, more comprehensive treatment becomes necessary. In addition, the doctors may also suggest additional medical treatments to address the underlying cause of the condition. Let’s have a look at the various treatments for hypoglycemia: Immediate Hypoglycemia Treatment If a patient experiences hypoglycemia symptoms, they should immediately consume 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, fruit juice, regular soda, honey, or sugary candy. Then, they must recheck the blood sugar levels after 15 minutes. If it remains below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), they must consume an additional 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates and test again in the next 15 minutes. If there is no improvement, the doctor will resort to other effective treatments. Severe Hypoglycemia Treatment In severe cases, medical intervention is necessary. The patients can use a glucagon injection or intravenous glucose to increase their sugar levels. If a patient does not have a glucose kit, it is essential to immediately reach out to the healthcare provider. Addressing the Underlying Cause To prevent recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia, the healthcare provider will likely identify and treat the underlying condition triggering it. Treatment may involve nutritional counseling to improve eating habits, adjusting or discontinuing medications if they are the cause, or addressing pancreatic tumors through surgery or medication, depending on the specific situation. Conclusion Severe hypoglycemia can be life-threatening, and therefore, it is essential for patients to seek timely diabetes treatment for the condition. Recognizing symptoms of this medical condition and seeking treatment is important to prevent serious complications and address any underlying condition. At Wockhardt Hospitals, we provide comprehensive treatment for diabetes hypoglycemia. To consult with our doctors, reach out to our team today.
Gestational Diabetes: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment

Gestational diabetes is a temporary diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and affects how the body processes sugar. Between weeks 24 & 28, gestational diabetes typically starts to manifest itself in the middle of pregnancy. The development of this type of diabetes does not imply that the woman had diabetes prior to becoming pregnant; it is generally due to hormonal imbalances caused by pregnancy. After giving delivery, a woman’s gestational diabetes disappears. However, it can elevate the risk of type 2 diabetes later in life and may have an impact on the health of the unborn child. Generally, gestational diabetes treatment depends on a healthy diet and regular exercise. Insulin is occasionally required for women who have gestational diabetes. Gestational Diabetes Causes When the body is unable to produce enough insulin to cope with the increasing demands of pregnancy, gestational diabetes develops. Several factors contribute to its development: Who is at Risk for Gestational Diabetes? Anyone who is pregnant has the potential to acquire gestational diabetes. But the danger is greater for individuals over 25. The following are other variables that might raise its risk: Gestational Diabetes Diagnosis Early diagnosis of gestational diabetes symptoms & management of gestational diabetes are crucial to ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Medical specialists advise screening for gestational diabetes around the 26th week of pregnancy or earlier if they have risk factors for the medical condition. The gestational diabetes diagnosis procedure typically involves the following steps: Gestational Diabetes Treatment The primary goal in gestational diabetes treatment is to maintain stable blood sugar levels, ensuring the health of both the mother and the baby. Treatment methods may include the following: Blood Sugar Monitoring It’s crucial to frequently monitor blood sugar levels. To ensure that the blood sugar remains within a safe range when a woman is pregnant, the doctor may advise checking the blood sugar four or more times each day, ideally first thing in the morning and after meals. Lifestyle Changes Our lifestyle, including what we eat and how much exercise we get, is crucial to maintaining appropriate blood sugar levels. Because the body is working so hard to support the developing baby, doctors typically advise against losing weight during pregnancy. However, based on the woman’s weight before pregnancy, a doctor can assist in establishing weight increase targets. Changes in lifestyle include: Medication In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to manage gestational diabetes. In such instances, the doctor may prescribe insulin or other medications to help regulate blood sugar. Foetal Monitoring Close monitoring of the infant is a crucial component of the treatment approach. For mothers with gestational diabetes, ongoing monitoring of the baby’s growth and well-being is essential. Ultrasound scans are frequently performed in this situation to check if the baby is growing at a healthy rate. If the mother doesn’t go into labour by the due date, the doctor may induce labour. Delivering after the due date may increase the risk of complications for the mother and the baby. Choose Wockhardt Hospitals for Best Diabetes Treatment & Management When it comes to visiting the right healthcare provider for gestational diabetes, Wockhardt Hospitals stands out as an excellent choice. Our team of experienced healthcare professionals, including obstetricians, endocrinologists, dietitians, and nurses, collaborates to provide comprehensive care. Modern diagnostic and monitoring tools are available at Wockhardt Hospitals, assuring the finest treatment for both mother and child. While gestational diabetes can be challenging to manage, early diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial for the well-being of both the mother and the baby. The causes of gestational diabetes vary; however, understanding these factors and their implications can help healthcare providers and expectant mothers take appropriate preventive measures.
Artificial Sweeteners & Diabetes: Any Effect on Blood Sugar

Artificial sweeteners are factory-made substitutes of sugar which provide the sweetness of sugar without the calories. Saccharin, aspartame, sucralose, neotame, and advantame are some of the common artificial sweeteners. These artificial sweeteners are made many times sweeter than normal sugar, due to which it takes only a small amount of artificial sweetener to produce the same effect as a spoonful of sugar. As a result of using a very small amount of sweetener, very few calories are consumed. There are many uses of artificial sweeteners and diabetes patients find it the most useful. However, artificial sweeteners are not quite as metabolically inert as previously believed. It has been claimed that artificial sweeteners can raise blood glucose and insulin levels, causing more complexities. Types of Artificial Sweeteners The types of artificial sweeteners which can be used for making low calorie sweeteners and diabetes patients can also use include the following. What Causes Rise in Blood Sugar Levels? There are many causes of rise in blood sugar levels: How Do Artificial Sweeteners Increase Blood Sugar Levels? Artificial sweeteners may not trigger a high rise in blood sugar levels in the short term. However, some studies have suggested that artificial sweeteners can cause a change in the balance of gut bacteria. These bacteria may change the ability of the cells and make them resistant to the insulin produced in the body, thereby increasing the levels of blood sugar as well as insulin in the body. However, when added to foods and drinks such as coffee and baked foods, the artificial sweetener may not raise the blood sugar level, but the other ingredients in such foods can do so as well as lead to an increase in fat content and calories. Can Artificial Sweeteners be Used by Diabetic Patients? Diabetes or prediabetes is caused by uncontrolled insulin production or due to insulin resistance, which raises the blood sugar level. Artificial sweeteners may not raise the blood sugar level. Hence, they can be used as a sugar substitute for diabetics but in moderation as per the doctor’s advice. When it comes to artificial sweeteners and diabetes, these sweeteners may not necessarily be labelled as “healthy”, but they are considered safer and “less bad” for consumption compared to refined sugar. Artificial sweeteners can be a good addition to maintaining a balanced diet. However, the different types of artificial sweeteners, such as sucralose, neotame, aspartame, etc., have varying effects on the level of insulin production. Therefore, it is better to consult a healthcare provider before starting with any artificial sweeteners for patients with diabetes or prediabetes. How Artificial Sweeteners Can Be Used by Diabetic Patients? People often tend to associate the rise in blood sugar levels as a problem. It doesn’t necessarily mean so. A spike in blood sugar level is a necessary process required by the body to produce the required energy for the body. However, it becomes a problem when the body is unable to bring the blood sugar level back to normal in a timely manner while the body becomes more resistant to the insulin produced by the body itself. This is what happens in people with prediabetes or type-2 diabetes. People living with prediabetes or diabetes likely already know how to manage blood glucose levels, and the first and foremost thing to adopt is to avoid sugar at all costs. But everyone experiences sweet cravings once in a while, so what should diabetic people do? To add sweetness to foods, diabetic patients can add artificial sweeteners instead of using regular sugar. When talking of artificial sweeteners and blood sugar, it is better to be gradual and moderate while including these sugar substitutes. It is definitely a good step towards a better health profile. Following this, diabetic and prediabetic patients can work on reducing how much or how often sweet foods are consumed. Even for people who are not diabetic, it is better to avoid getting blood sugar spikes frequently as it may lead to diabetes in the long term and make it tougher to lose weight. Get Best Medical Help at Wockhardt Hospitals The best way to understand your blood sugar levels if you are concerned is to get a blood sugar test done by visiting the highly experienced doctor or healthcare provider at Wockhardt Hospitals. Comprehensive medical consultation and precise diagnostic testing will help understand if any changes need to be made in food habits and lifestyle to avoid developing diabetes. For consultation with the best primary care doctors in India for diabetes treatment, book your appointment at Wockhardt Hospitals, Mumbai, Maharashtra and get a complete sugar profile test with accurate evaluation and analysis.
Cataracts: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment

What is Cataract Surgery? Cataract surgery is a medical procedure performed to remove the affected cloudy lens in your eyes. The lens is affected by protein breakdown in the eyes, causing the lens to become cloudy and blurred. Cataracts increase glare by preventing light from passing through the lens, which might affect your daily activities. When a cataract interferes with your normal life, the highly experienced doctors and eye surgeons at Wockhardt Hospitals might suggest cataract surgery. A cataract surgery procedure is the only sure-shot way to treat this condition in adults. Cataract surgery in India is done on an outpatient basis by a certified ophthalmologist and is a very common and safe procedure. We at Wockhardt Hospitals have performed a large number of successful cataract surgeries giving patients their vision back. Our ophthalmologists and surgeons are board certified and are backed by world-class medical facilities and well-trained staff to give the desired surgical results. Signs & Symptoms of Cataracts Typically, a cataract condition develops slowly. A person might not even be aware of their presence until they begin to block the light. As the symptoms start to surface, they might experience – Once these symptoms start interfering with the regular lives of a person, they immediately need a cataract treatment. Causes of Cataracts Cataract surgery in India is done to treat cataracts that cause a variety of symptoms, including blurry vision, floaters, itching, etc. The majority of cataracts occur when the tissue of the eye’s lens changes due to aging or trauma. The lens’s proteins and fibers start to degrade, clouding or obscuring the vision. The risk of cataracts may be increased by hereditary and/or genetic abnormalities resulting in other health issues. Other eye diseases, previous eye surgery, or medical conditions, especially Diabetes, might also lead to cataracts. Also, the long-term use of steroid medicines can also result in cataract development. Cataract Surgery – Dos & Don’ts Usually, the doctors advise the patients regarding dos and don’t during the final consultation before the surgery. However, even after the surgery, the doctors will reiterate the precautions that must be taken after cataract treatment. Some of the most important dos & don’ts are mentioned below – Dos Don’ts What Tests are Done to Diagnose Cataracts for their Effective Treatment? To determine if you have a cataract, the doctor will physically examine your eyes, and to rule out other eye conditions, they will order the following cataract diagnostic tests – Treatment of Cataracts The only effective treatment for cataracts is surgery; however, you might not require it immediately. You might be able to get by with a fresh prescription for your glasses if you identify the issue early. However, the need for surgery depends on how critical the condition is. If the cataract is diagnosed at the early stage, cataract can be taken care of by prescription glasses with stronger lenses to help the patient see clearly. Though there are several types of cataract treatment procedures, all of them have one thing in common – the doctor replaces the cloudy and blurry lens with an artificial lens. It is a very common procedure and is generally safe. Doctors use local anesthesia to numb the eyes before the operation. Hence, the patient will not feel anything. The surgery usually takes less than 60 minutes, and the patient will be discharged on the same day. Also, if the cataract is in both eyes, the doctors will first perform the cataract operation procedure in one eye, and after it heals, they will continue with the other one. Here’s a detailed process of the surgery performed at Wockhardt Hospitals- The lens is then divided into several tiny fragments by the surgeon using ultrasonic waves, and the pieces are vacuumed out. Also, the cataract surgery procedure does not require sutures. The patient’s vision starts to improve a few days after cataract treatment. As the eye adjusts to the injury and heals, the vision may initially be blurry. After the cataract operation procedure, they may notice a bright and clearer view. This is because of the fresh and new lenses. After having a cataract surgery procedure, the majority of people use glasses, at least occasionally. When the eyes have recovered sufficiently to receive a final prescription for glasses, the doctor will let you know. This often occurs one to three months following surgery. To manage inflammation, reduce eye pressure, and prevent infection, the doctor may advise eye drops or other medications. These drugs may occasionally be administered into the eye during surgery. How Long Does it Take to Heal after Cataract Surgery? Every individual’s body is different, which means the amount of time it will take to recover also varies. At first, you might have a blurry vision as your eyes are in their healing process. Take time to recover, and try giving your eyes the maximum amount of rest. Usually, the eyes start to get better within 1 to 2 days, but it is advisable not to perform any heavy task which might cause stress to your eyes. Also, it is prohibited not to lift heavy objects or bend. Talk to your doctor when you can return back to work. They will tell you an estimated time when you can resume work. Most patients fully recover and heal in around eight weeks after the surgery. After the procedure, your doctor will schedule a few follow-up visits to check on your recovery and to ensure you are healing well. Risk Factors for Cataracts The surgery performed at Wockhardt Hospitals under the supervision of highly experienced eye surgeons usually does not cause any serious complications. It is done under topical anesthesia with eye drops. But, just like any other surgery, it also has some risk factors which increase the chance of complications. Below are some of the risk factors for your reference- FAQs on Cataracts Q. Which surgery is best for cataracts? FLACS, or Femto Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery, is a new innovative technique and is considered the best.
Breast Cancer Signs, Symptoms & Causes

Breast cancer is the second most common type of cancer in women; it originates in the breast. Breast cancer can also affect men, but it’s relatively more common in women. The causes of breast cancer may range from increasing age and a history of cancer in the family to the inheritance of mutations in the genes, starting periods early, etc. Out of the various types of cancers in women, breast cancer is the second leading cause of death. The chance of a woman dying from breast cancer is roughly 1 in 39, which is about 2.5%. Breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body through blood and lymph vessels. When this happens, it’s called metastasis. Recognising breast cancer symptoms in time can help prevent the condition from worsening and stop potential metastasis. Types of Breast Cancer Oncologists determine the type of breast cancer that has occurred in a patient to tailor an appropriate treatment plan that is effective but has the least possible side effects. The common types of breast cancer that can affect women include the following: Lobular Breast Cancer: This type begins in the milk-producing glands called lobules and tends to spread to nearby breast tissues. Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): Another type that begins in the milk ducts and spreads to nearby breast tissues. Ductal Carcinoma in situ (DCIS): Similar to IDC, it begins in the milk ducts but does not spread to surrounding tissues. Triple-negative Breast Cancer: An invasive form of breast cancer that spreads more quickly than other types. Inflammatory Breast Cancer: A rare, fast-growing form that resembles a rash on the breast. Paget’s Disease: A rare breast cancer that affects the skin of the nipple and appears as a rash. What Causes Breast Cancer? There are several reasons why a person may develop breast cancer, and breast cancer causes typically vary from person to person. Our body normally replaces old cells with new ones at a set pace. But in breast cancer, the body’s natural control system becomes dysfunctional, causing a fast and abnormal cell growth. While there’s no single cause of breast cancer, certain factors put women at an increased risk of developing this kind of cancer, including: The woman’s age: Breast cancer is typically reported in women who’re over the age of 50. The risk of breast cancer increases as women age. A Family History of Breast Cancer: If there’s a history of breast cancer in the family, the respective woman may be at an increased risk of developing it. The chances are higher if her mother or sister had developed breast cancer before their menopause. In addition, if a woman has had breast cancer in the past, she may be at an increased risk of developing it again. Age of Pregnancy: Women who’ve had their first child after the age of 30 are at a higher risk of breast cancer. In addition, those who’ve not given birth till or after 30 may be at more risk. Age of Menstruation: Women who got their periods before 12 are more prone to developing breast cancer in the future. Late Menopause: Women who’ve experienced a late menopause, typically after the age 55, stand at a higher risk of developing breast cancer. Radiation Treatment: The risk of breast cancer elevates if a woman has undergone chest radiation treatment at some point in her life. Unhealthy Lifestyle: Being obese or overweight, improper dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and unmonitored or regular consumption of alcohol are also among the leading causes of breast cancer. Using hormone replacement therapy or HRT for a long time can also put a woman at a higher risk. Breast Cancer Signs and Symptoms Breast cancer may or may not exhibit any symptoms, depending on its stage. In addition, the breast cancer symptoms and their severity may differ for every patient. Some commonly reported breast cancer signs and symptoms are as listed below: A Painless Lump in the Breast: This is the most common symptom of breast cancer. It may feel like a pain-free mass in the breast or underarm. For early diagnosis, women are advised to carefully assess their breasts for lumps as part of a habit. Dimpled or puckered skin on the breast: Sometimes, dimples or puckered skin on the breast may also indicate breast cancer. In addition, a change in the texture of the breast skin can also be indicative of breast cancer or another underlying condition. Bleeding or Unusual Discharge from the Nipple: Bleeding from nipples can be eerie and a possible sign of breast cancer. Also, any other abnormal discharge that is clear or has an unusual colour can be a cause of concern and requires prompt medical attention. A Change in the Size of the Breast or Nipple: Breast cancer can also cause the breast’s shape to change. Patients can see a difference in the shape of both breasts. Itchiness and a rash around the nipple that does not go away: A persistent urge to itch around the nipple can also be a sign of breast cancer. Contact a doctor if the itchiness of rashes around the nipples does not get better with medication. A pulled-in or retracted nipple: If the nipple suddenly becomes inverted or retracted, it’s concerning and requires a doctor’s intervention. Swollen and thickened skin over the breast: When the skin over the breast becomes swollen or noticeably thicker than usual, it may be a sign of a problem. This change in skin texture should be examined by a healthcare professional. Conclusion Breast cancer is a serious health issue that requires prompt diagnosis and timely treatment. If you notice breast cancer symptoms, as mentioned above, make sure you seek immediate medical intervention. For top-notch diagnostic and treatment facilities, you can reach out to the medical experts at Wockhardt Hospitals. We have a team of the best oncologists in India, with extensive experience in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Experts at Wockhardt Hospitals chalk out a personalised treatment plan for all patients, based on the specific requirements of their respective cases. Comprehensive and round-the-clock patient care is at the
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment, Surgery

Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women. It occurs inside the breasts when cancerous cells grow and multiply leading to the formation of tumours. It typically affects women above 50 years of age but women younger than 50 may also get breast cancer. Breast cancer may grow and spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Oncologists treat breast cancer through surgery or other treatment methods to kill cancer cells. The type of treatment given depends on the type of breast cancer affected and the stage of cancer. Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Breast cancer diagnosis is performed by a doctor who may ask about the symptoms as well as the medical and family history of the patients. They may recommend several tests and procedures to diagnose or rule out breast cancer. Staging Breast Cancer If diagnostic tests have detected cancer in the breasts, staging the cancer is necessary to understand how far it has spread. Staging is essential for determining the prognosis and devising an appropriate treatment plan customised to an individual’s needs. Breast cancer stages are as follows: Treatment of Breast Cancer Breast cancer surgery is the primary form of breast cancer treatment, but oncologists may recommend additional cancer treatments depending on the specific requirements of each case. However, the form of breast cancer treatment is based on the type, size, and stage of breast cancer. Surgical treatments used to treat breast cancer include the following: There are many other methods used for the treatment of breast cancer, such as: Chemotherapy Chemotherapy treatment uses drugs to destroy fast-growing cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be recommended before or after surgery, depending on the specific requirements of the patient. If there is a chance of recurrence, chemotherapy may be performed after surgery. If breast tumours are larger, chemotherapy may be required before surgery to prevent cancer from spreading to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy may also be used to control symptoms of breast cancer. Radiation Therapy Radiation therapy makes use of high-energy X-rays or other particles to destroy cancer. External-beam radiotherapy may be performed after a lumpectomy and mastectomy procedure if the tumours are larger or have spread to the lymph nodes. Hormone Therapy Hormonal therapy is utilised to treat breast cancer sensitive to specific hormones. These cancers may be oestrogen receptor-positive (ER positive) or progesterone receptor-positive (PR positive). Hormonal therapy may be used before or after surgery or other cancer treatments to prevent cancer recurrence. This treatment may also help arrest the spread of cancer and shrink it. Targeted Therapy Targeted therapy uses drugs to identify and attack specific abnormalities within cancer cells. This procedure may be used after surgery to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence. Immunotherapy Immunotherapy involves fortifying the body’s own immune system to fight off cancer by interfering with the process of producing proteins that help cancer cells grow. Triple-negative breast cancer may be treated using immunotherapy. Palliative Care Palliative care is a specialised supportive treatment that focuses on providing relief from pain and other cancer symptoms. Palliative treatment may be provided when treating advanced breast cancer or aggressive forms of treatment, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy. The aim of palliative care is to improve the quality of life of cancer patients while offering curative treatments. Conclusion Breast cancer may be cured by early detection and prompt treatment. However, breast cancer may come back, and when it does, it may become metastatic; that is, it may start spreading to other parts of the body. Get the best breast cancer treatment in India at Wockhardt Hospitals for all-round comprehensive cancer care by the top Oncologists who have extensive experience in treating cancer for many years. Contact us directly and get the best quote on breast cancer treatment cost in India. FAQs on Breast Cancer Treatment in India Q. What is the cost of breast cancer treatment in India? To determine the location, extent, and spread of cancer, an imaging test is conducted. The initial fee for a cancer evaluation is 35,000 to 45,000 rupees. The patient’s treatment strategy will be discussed by the oncosurgeon based on the results of the medical test. In India, breast cancer treatment costs start at 2 lakhs to 4 lakhs. Q. How to perform a home test for breast cancer? Also known as breast cancer self-examination, it involves women feeling their breasts once a month to check for lumps, thickening, firm knots, or other abnormalities. Watch out for any swelling, changes in nipple orientation, peeling, or sores. Also, look for fluid leakage from the nipples. Q. Does breast cancer metastasize quickly? Breast cancer staging and grading can provide some indications of the malignancy’s aggressiveness. For instance, compared to grades 1 and 2, grade 3 breast cancer has a higher chance of spreading rapidly. Since stage 4 breast cancer has already spread outside the breast tissue, it is, by definition, the fastest-spreading type.
Tongue Cancer Symptoms, Causes, Signs & Treatment

Tongue cancer begins with the uncontrolled growth of cells on the tongue. The tongue extends from the neck into the mouth and is composed of nerves and muscles that support various functions, such as taste, speaking, eating, and swallowing. The tongue can be affected by various types of cancers, with tongue cancer often originating in the flat, thin squamous cells that cover its surface. This condition is referred to as squamous cell carcinoma. When devising a treatment strategy, the doctor considers the type of cancer cells involved. Common treatments for tongue cancer include surgery and radiation therapy, while chemotherapy and targeted treatment may also be considered as alternative options. Tongue Cancer Causes The DNA of healthy tongue cells alters, which is the first sign of tongue cancer. The instructions for what a cell should perform are encoded in its DNA. When healthy cells would normally die as a part of their regular life cycle, the modifications signal the cells to grow out of control and to stay alive. As a result, many additional cells are produced. A development known as a tumour can develop from these cells. These cells have the potential to separate over time and spread to other parts of the body. The changes that lead to tongue cancer are not usually easy to pinpoint. The human papillomavirus, or HPV, may play a role in certain throat-based tongue cancers. Sexual contact is the primary method of transmission for the widespread HPV virus. The following are the most common tongue cancer causes: Types of Tongue Cancer There are two sections on the tongue. The oral tongue is the front two-thirds of the tongue, while the base tongue is the remaining third. One kind of tongue cancer is oral tongue cancer. The most typical kind of cancer of the tongue is squamous cell carcinoma. Tongue cancer that develops in the mouth differs from tongue cancer that develops in the throat. Tongue Cancer Symptoms The following tongue cancer signs may appear if it spreads to other areas of the oral cavity, such as the floor of the mouth, gums, jawbone, or deeper muscles: Signs of Tongue Cancer Tongue cancer may not initially exhibit symptoms. In certain cases, a doctor or dentist may detect tongue cancer early signs during a routine examination while searching for indications of mouth cancer. These tongue cancer early signs typically involve the presence of a non-healing sore on the tongue. Other potential signs include the development of a tumour or thickening on the tongue, as well as experiencing pain or bleeding in the mouth. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck could serve as an initial symptom of tongue cancer that has spread to the throat. Additional signs to watch for may include earaches, weight loss, and episodes of bloody coughing. Another tongue cancer early signs is the presence of a lump in the neck, throat, or the back of the mouth. Other tongue cancer signs may include: Tongue Cancer Treatment Radiation, chemotherapy, or both may be used in addition to surgery as a treatment for tongue cancer. An effective treatment plan is developed after a thorough evaluation of many criteria by your healthcare team. The cancer’s location and growth rate are two such factors. Your body’s overall cancerous status and the outcomes of any tests performed on the cancer cells may also be examined by the team. Age and general health are other factors that are taken into consideration. Here are the treatment options. Surgery – Depending on the size of the cancer, a surgeon may remove all or part of your tongue during the procedure, known as a Glossectomy. A few healthy cells that surround your tongue will also be removed. You could require physical therapy and rehabilitation following surgery to address speech and swallowing issues. Reconstructive Surgery – When a cancer procedure requires the removal of certain features of your mouth or face, doctors can reconstruct those tissues using this kind of surgery. Healthy bone or tissue from other sections of your body will be substituted for lost tongue, lip, and facial tissue. Radiation Therapy – This treatment targets particular areas of the body with powerful energy beams from protons, X-rays, or other sources to destroy cancer cells. Targeted Therapy – By targeting certain molecules within cancer cells, targeted therapy destroys the cancer cells. It can be used to treat tongue cancer that has returned or spread outside of the original tumour by medical professionals. Chemotherapy – In order to stop cancer cells from growing or to eradicate any remaining cells, you will take medication either before or following cancer surgery. Immunotherapy – Your doctor may recommend immunotherapy if other therapies aren’t working for your advanced tongue cancer. It manifests by assisting your immune system in identifying and eliminating cancerous cells. Conclusion If you suspect that you may have tongue cancer or are concerned about the risk factors, it is crucial to promptly seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment of tongue cancer causes and symptoms offer the best chances of a successful outcome. Our team of doctors at Wockhardt Hospitals consists of recognised and highly qualified cancer care experts who can provide personalised guidance and recommendations based on your specific situation. Our team’s aim is to ensure that patients receive the best possible treatment for tongue cancer while minimising the risk of complications. FAQs on Tongue Cancer Q. What are the first signs of cancer of the tongue? A lump or thickening in the tongue, continuous mouth ulcers, pain in the tongue, trouble swallowing or chewing, and abnormalities in speech or voice are usually the initial symptoms of tongue cancer. For prompt treatment, early diagnosis through routine dental exams is essential. Q. Can cancer of the tongue be cured? Radiation therapy or surgical excision are two treatment options for tongue cancer in its early stages. Glossectomy is one type of surgery that can remove all or part of the tongue. In cases with more advanced stages, radiation treatment and chemotherapy may come after